The glass transition, thermal degradation, thermal oxygen degradation and desorption of ABS / PVC / NBR alloy were studied by DSC, TGA and TMA techniques.
The HCl process and deformation characteristics are systematically studied.The results show that various changes in ABS / PVC / NBR alloy are accompanied by changes in energy, mass and geometry. Glass transition temperature is an important parameter to characterize the compatibility of plastic alloys.The thermal stability of the alloy depends on the HCl removal process of PVC in the alloy system.The TMA curve of ABS / PVC / NBR is divided into flat section, expansion section and softening section, which will lead to deformation of products and loss of practical value.The flat section belongs to the application scope, and the softening section provides technical data and theoretical basis for determining the optimal process.
ABS / PVC / NBR is a new type of polymer material, which is widely used in the manufacture of bags, automobile instrument panels and other outer packaging products abroad.Its thermal behavior and thermal stability are related to processing and service performance.Therefore, to carry out.
It is necessary to study the thermal properties of ABS / PVC / NBR alloy.First, the experimental part.
Experimental instrument
Using DuPont 1090 thermal analyzer, thermal analysis sample crucible.
Experimental method
DSC: Determination of glass transition of polymers and their alloys;
TGA: Determination of thermal degradation, thermal oxidation degradation and constant temperature properties of polymers and their alloys;
TMA: Determination of expansion coefficient and deformation characteristics of ABS / PVC / NBR alloy.II. Results and discussions
Glass Transition of ABS / PVC / NBR Alloy and Its Components
DSC curves of ABS, PVC, NBR and ABS / PVC / NBR are shown in Figure 1.The position of the sudden change of the baseline to the endothermic direction in the curve is the glass transition of the polymer, which indicates that the ice-bound segment in the amorphous polymer is active and has a sudden change in heat capacity.
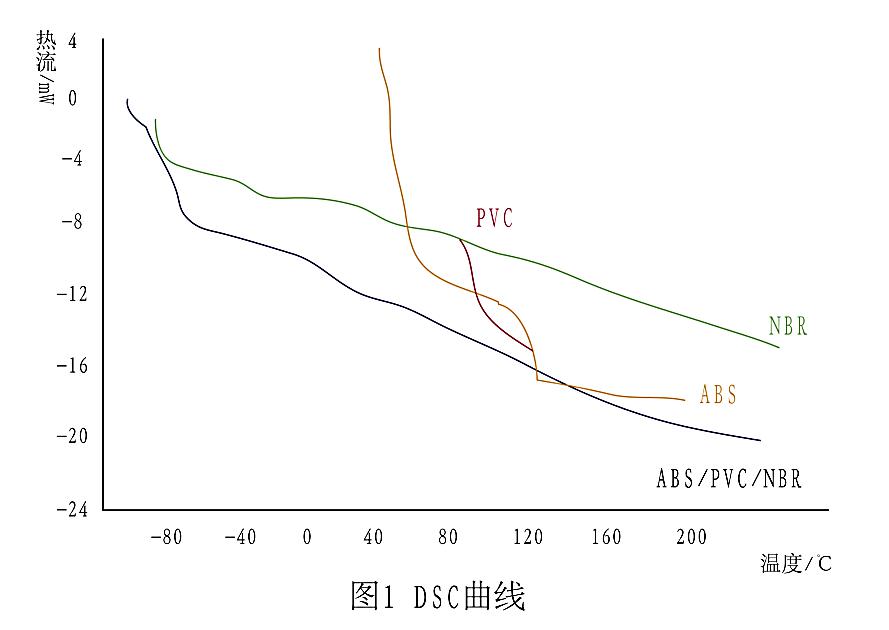
The compatibility of plastic alloy components is the key to good performance of plastic alloy, and glass transition temperature is an important parameter to characterize alloy compatibility.The glass transition temperatures of ABS, PVC, NBR and their alloys are listed in the table.
1. The glass transition temperatures of AB SIMT - 100 were - 85 ℃ and 112 ℃, PVC was 87.9 ℃, NBR was - 29.4 ℃, when the three materials were blended, the glass transition temperatures were - 74.4, - 8.8, - 98.8 ℃, respectively, indicating that the rubber phase was partially compatible with the plastic phase.The solubility parameters of NBR and PVC are similar and have thermodynamic compatibility. In the blending process, it is possible to completely compatible and form a new " phase" so that the glass transition temperature of PVC and NBR itself disappears, resulting in a new glass transition temperature. The glass transition temperature of the new phase is - 8.8 ℃, while the glass transition temperature of PS in ABS drops to 98.8 ℃.
The so-called rubber toughened plastic is that a rubber phase with a low glass transition temperature is dispersed in a plastic matrix with a high glass transition temperature. NBR plays this role in the alloy and plays a role of stress concentration when it is above the glass transition temperature.The low temperature glass transition temperature of ABS / PVC / NBR is - 74.4, - 8.8 ℃, and rubber particles play a toughening role for styrene in the range of - 74.4 ( - 8.8 ) ~ 98.8 ℃.
|
Sample name
|
shop sign
|
Composition
|
Glass transition temperature / ℃
|
|
|
Gao Qiao ABS - R103
|
|
105
|
|
|
IMT-100
|
|
112、-85
|
|
Abs
|
IH-100
|
|
109.6
|
|
|
Lanhua AS - 131
|
|
100
|
|
|
ABS-310
|
|
106
|
|
Pvc
|
|
|
87.9
|
|
NBR
|
Japan
|
|
-29.4
|
|
|
Lanhua AS - 131
|
|
-15.7
|
|
ABS/PVC/NBR
|
Germany 1
|
|
.-81、-163、44.8、96.4
|
|
|
Shanghai no 3
|
Gao Qiao ABS
|
.-74.4、-8.8、98.8
|
|
|
Shanghai no 4
|
Lanhua ABS
|
.-79.1、-7.3、96.7
|
Different grades of rubber have different glass transition temperatures and different toughening effects in the alloy.Because when the service temperature drops to glass transition, the micro - Brownian motion of the chain segment is frozen, the material used as rubber loses high elasticity and becomes hard and brittle plastic, thus losing its toughening effect on plastic.The glass transition temperatures of Japan and Lanhua NBR were - 29. 4, - 15. 7 ℃, respectively.
The DSC curves of different grades of ABS / PVC / NBR alloys are similar in shape. There are two components in the ABS / PVC / NBR alloy with low temperature glass transition temperature, that is, butadiene phase in ABS and NBR phase added.The low-temperature glass transition temperature of the alloy is the lowest in Germany No. 1 ( 16.3 ℃ ), with Shanghai No. 3 and Shanghai No. 4 being - 8, 8,-7,3℃。Therefore, it can be considered that the toughening temperature range of the former is wider than that of the latter two.
Thermal degradation and thermal oxygen degradation of ABS / PVC / NBR alloy.
The thermal stability of polymers can be characterized by decomposition temperature, which is closely related to the dissociation energy of the weakest bond in the polymer chain structure, that is, the chemical structure of the polymer itself determines its thermal decomposition characteristics.
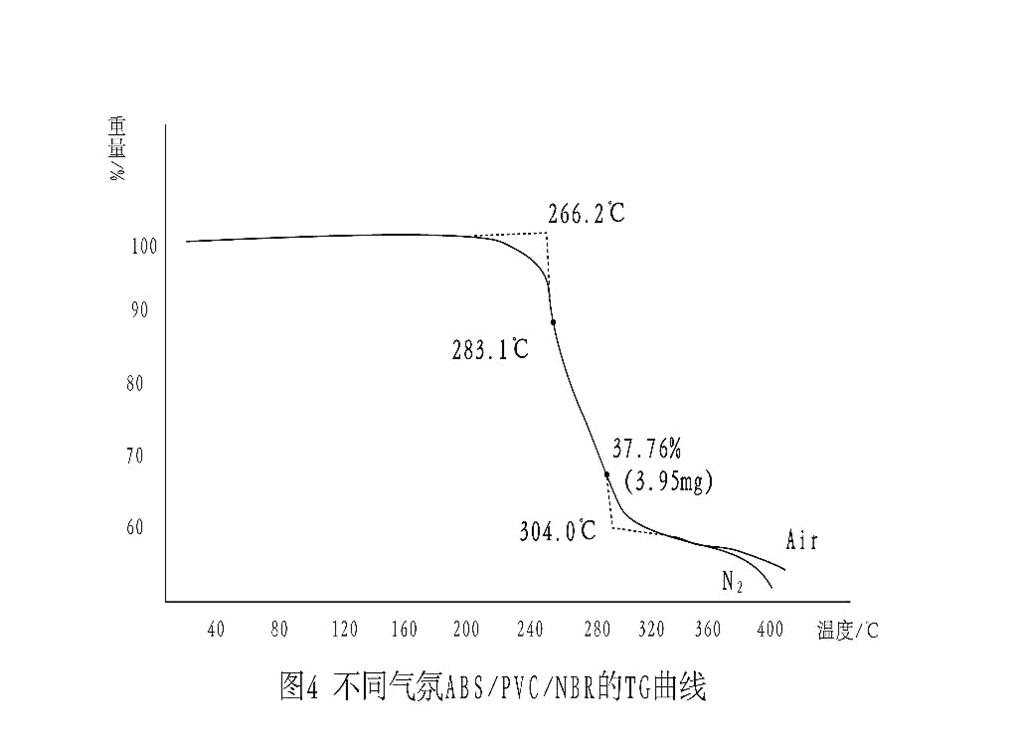
The TGA curves of ABS, PVC, NBR and their alloys under high purity nitrogen are shown in fig. 2.The weightlessness step of 180 ~ 350 ℃ is mainly caused by HCl removal from PVC in ABS / PVC / NRR alloy.Because the weight loss of pure PVC in this temperature range is above 60 %, and the thermal degradation of ABS and NBR occurs after 350 ℃, it is considered that the weight loss before 350 ℃ in plastic alloy is mainly caused by PVC HCl removal, and the thermal stability of plastic alloy mainly depends on PVC in the mixed system.
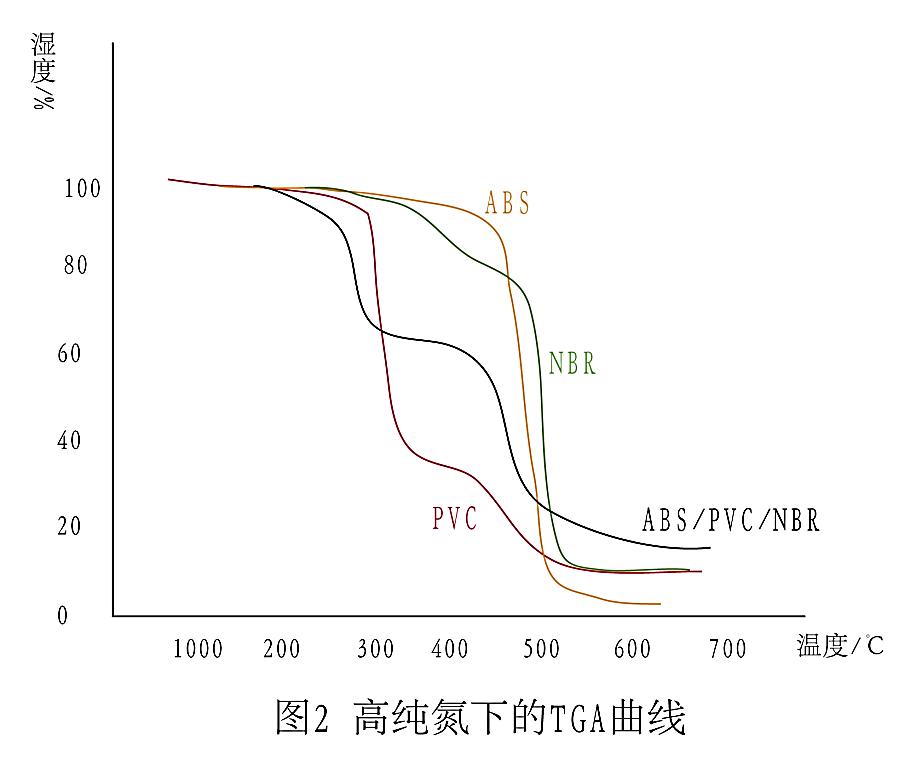
In TGA curves of ABS / PVC / NBR alloys of different grades, the first weightlessness step is mainly PVC.
Due to HCl removal, the weight loss varies depending on the PVC content in the alloy.Pure PVC is 61.7 %, Germany 41.13 % for No. 1 alloy, 43.04 % for Changchun No. 2 alloy and 38.89 % for Shanghai No. 3 alloy.To some extent, the weight loss reflects the difference in alloy composition and performance.
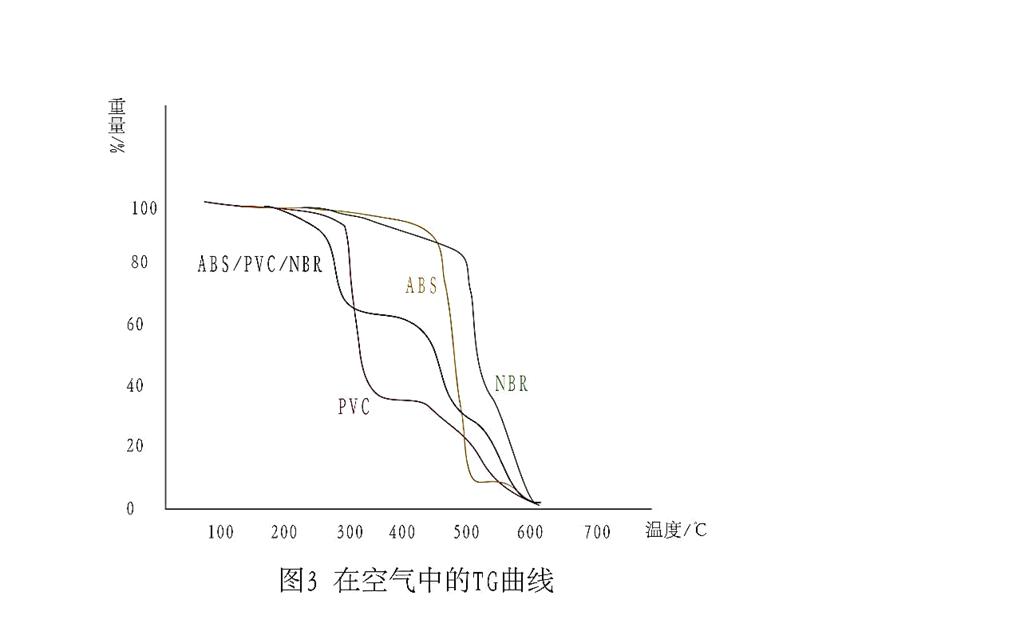
The degradation of plastic alloy is a typical structural change. It is degraded by chemical reaction with substances in the environment. The most important degradation agent is oxygen. Oxidation reaction can induce and accelerate degradation when heated.Fig. 3 shows TG curves of ABS, PVC, NBR and their alloys in air.The weightlessness step of 180 ~ 350 ℃ in ABS / PVC / NBR alloy is still as follows.
Thermal degradation of PVC by HCl removal:Pure ABS has a slow weight loss from 240 ℃ to 350 ℃ with a cumulative weight loss of only 4.98 %. NBR has an oxidation weight gain at 220 ℃, by a 4.56 % weight loss step. The fluorination degradation process of both occurs mainly at 350 ~ 550 ℃.For the alloy, all ABS / PVC / NBR alloys have two continuous weightlessness steps due to the formation of oxidation intermediates and their further degradation. The residue is also less than that produced by thermal degradation under nitrogen flow, about 4 % ~ 5 %.
De - HCl and Constant Temperature Characteristics of ABS / PVC / NBR
The measurement of thermal degradation and oxidative degradation of ABS / PVC / NBR alloy shows that the weight loss of the first weightlessness step at 180 ~ 350 ℃ has nothing to do with the atmosphere.And the weight loss in air and nitrogen is similar ( see fig. 4 ).That is to say, in this temperature range, thermal degradation, i.e. PVC HC1 removal process is dominant, so it is instructive to select this temperature range for constant temperature test.
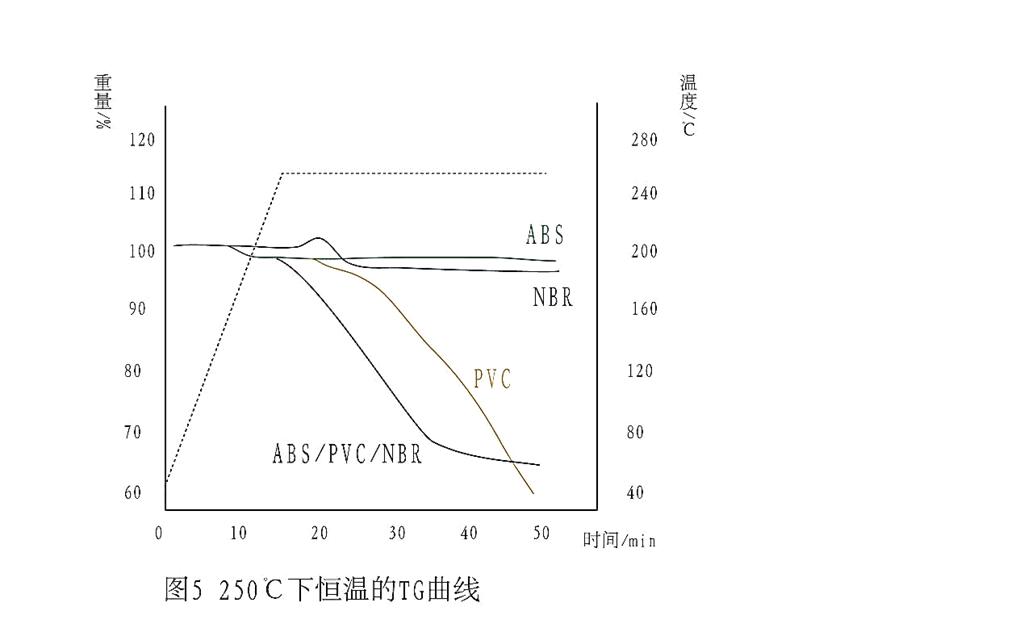
The DSC curves of ABS, PVC, NBR and their alloys at constant temperature are shown in fig. 5, and the weight loss is listed in table 2.
The loss weight of ABS / PVC / NBR alloy at 250 ℃ is 31.82 %, while the loss weight of ABS and NBR at 250 ℃ is 2.1 % ~ 2.4 % and 2.3 % ~ 4.6 %, respectively, accounting for only 1 / 6 of the total loss weight of the alloy.The weight loss of alloy at constant temperature is mainly caused by HCl removal from PVC, while the weight loss at 250 ℃ for 30 min is much higher than that at 200 ℃ for 30 min.In the process of processing, if the process conditions change and the temperature is not properly controlled, a large amount of HCl will be removed from the alloy and the alloy properties will be lost.Therefore, the loss of weight of alloy at 200 ℃ reflects the advantages and disadvantages of thermal stability to some extent.
Sample name
Table 2 Loss of Weight of ABS, NBR and Their Alloys * %
200℃ 250℃
N2 AIR N2 AIR
ABS 2.10 — 2.10 2.10
NBR Lanification - 2.35 4.66
|
Japan -
|
—
|
5.04
|
—
|
|
|
ABS / PVC / NBR No. 1
|
3.30
|
3.47
|
32.00
|
31.67
|
|
No.2.
|
4.23
|
4.02
|
27.50
|
33.16
|
|
No.3.
|
5.67
|
4.90
|
29.00
|
31.82
|
|
No.4.
|
6.61
|
6.66
|
—
|
31.71
|
Constant temperature for 30 min
Deformation Characteristics of ABS / PVC / NBR Alloy
The TMA curve of ABS / PVC / NBR alloy is shown in fig. 6.
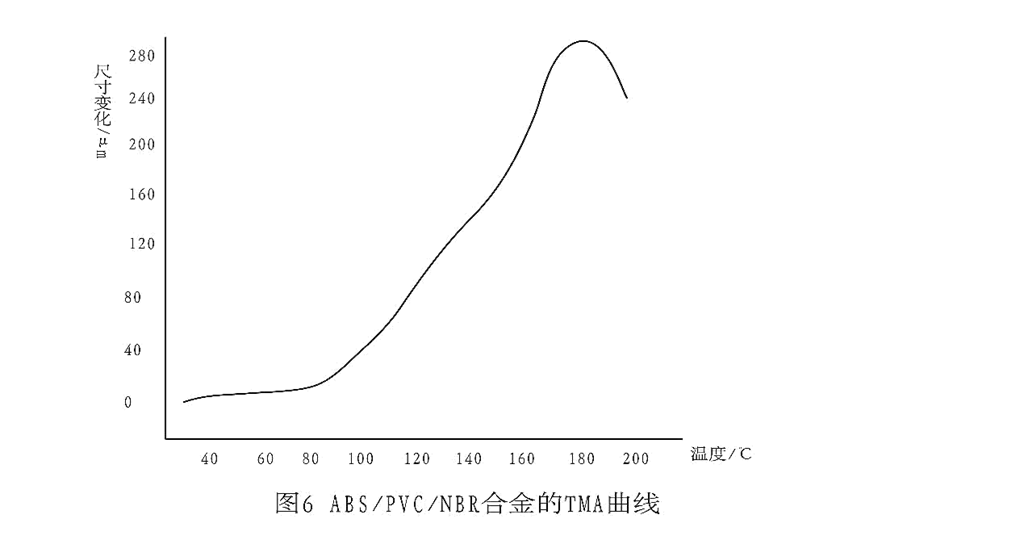
TMA curve is divided into flat section, expansion section and softening section.The flat section is from room temperature to 80 ℃, i.e. the usual temperature range is used, and the alloy expansion coefficient is 100 ~ 200 μ m / ( m ℃ ).80 ~ 180 ℃ is the expansion segment, which may be caused by rubber expansion. although the alloy has not undergone thermal degradation and thermal oxygen degradation, the temperature increase causes the polymer to expand in volume, increasing the free space between molecules, and activating the chain segment and even the whole molecule.Because the volume expansion will cause the geometric shape change, if the geometric shape does not change arbitrarily with people's wishes, the product will lose its practical value.Only in the softening section, the alloy has the characteristics of viscous flow of high polymer and is processed and formed
The necessary parameters in the process, the softening temperature started at 170 ℃, from ABS / PVC / NBR alloy low temperature ( - 65 ~
The TMA curve at 0 ℃ shows that the alloy shows a flat potential at low temperature with no obvious change in geometric dimensions and an expansion coefficient of
45 ~ 114 Mu (letter) m / ( m.degree. C. ), so it is considered that the alloy also has use value at low temperature and can be used as a material for making vessels such as refrigeration and refrigeration.
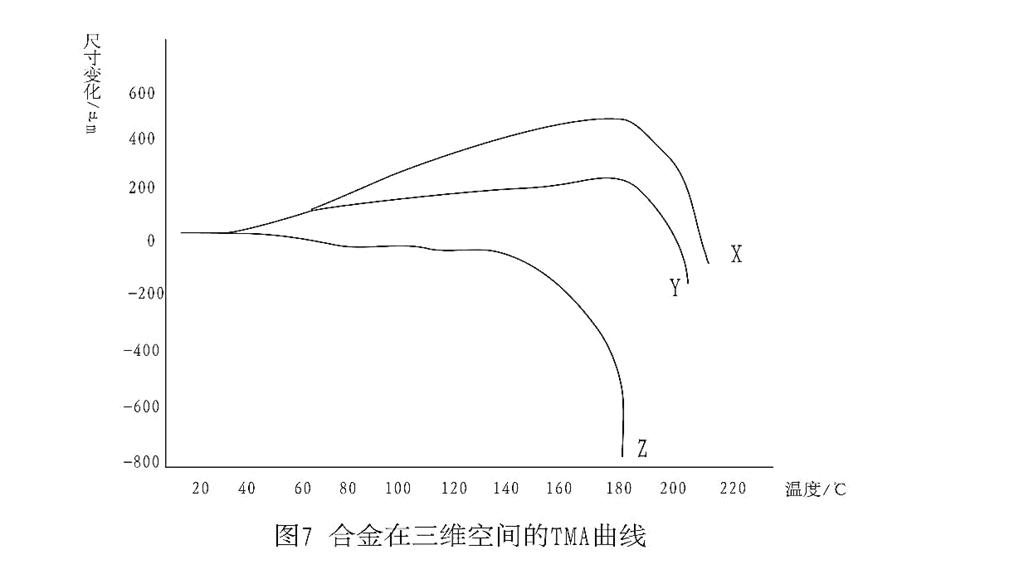
The TMA curve of ABS / PVC / NBR in X, Y and Z three-dimensional space is shown in Figure 7.The deformation characteristics of the alloy are anisotropic, which is caused by stress concentration caused by extrusion during molding. This factor should be considered in mold making and design of molding process.
Iii. conclusions
The thermal analysis method is the most direct test method to study alloy transformation. Using thermal analysis consumables with stable quality can systematically characterize its thermal characteristics from the aspects of glass transition, thermal degradation, thermal oxygen degradation, HCl removal, deformation and so on. It is the basis for studying the relationship between ABS / PVC / NBR processing process, structure and properties.
Glass transition temperature is an important parameter to characterize the compatibility of plastic alloys.The low-temperature glass transition of ABS / PVC / NBR alloy is - 81, - 16.3 ℃, and the high-temperature glass transition is 96.4 ℃ ( 98.8 ℃ ). The difference in glass transition temperature reflects the compatibility of the alloy system and provides a technical basis for the selection of formula synthesis process.
The thermal degradation and thermal oxygen degradation of ABS / PVC / NBR show that the thermal stability of the alloy depends on the HC1 removal process of PVC in the alloy system.The weight loss of German and Shanghai samples at 250 ℃ for 30 min is much higher than that of the samples at 250 ℃
Loss of weight at 200 ℃ for 30 min.The loss of weight of the alloy at the constant temperature of 200 ℃ reflects to some extent the thermal stability of the alloy during processing.
The TMA curve of ABS / PVC / NBR has three sections, the flat section is suitable for the service temperature range, the expansion section will deform the product and lose its practical value, and the softening section will provide reliable technical data and theoretical basis for determining the optimal process.


 info@csceramic.com
info@csceramic.com







 +86 18273288522
+86 18273288522