Alumina Ceramic Crucibles Used For Melting Precious Metals
In the world of metallurgy and materials science, the choice of crucible for melting precious metals is of paramount importance. The crucible serves as the vessel where metals undergo transformation from solid to liquid, and its properties can greatly influence the outcome of the melting process. One intriguing option that has gained attention is the alumina ceramic crucible. In this article, we'll delve into the characteristics, benefits, and considerations surrounding the use of alumina ceramic crucibles for melting precious metals.
Introduction
When it comes to melting precious metals like gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, the choice of crucible is crucial. Alumina ceramic crucibles have emerged as a fascinating option due to their unique properties and potential benefits.
Properties of Alumina Ceramic Crucibles
Alumina ceramic crucibles are crafted from alumina, a highly refractory material. They boast excellent thermal stability, withstanding high temperatures without significant deformation. The non-reactive nature of alumina minimizes the risk of contamination, ensuring the purity of the melted metals.

Advantages of Using Alumina Ceramic Crucibles
Temperature Resistance
Alumina crucibles can endure extreme temperatures, making them suitable for high-temperature melting processes.
Chemical Inertness
The non-reactive nature of alumina prevents unwanted chemical reactions between the crucible and the melted metals.
Purity Preservation
Alumina ceramic doesn't impart impurities, safeguarding the integrity of precious metals.
Thermal Shock Resistance
The crucibles can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, prolonging their lifespan.
Considerations for Melting Precious Metals
As an expert in the field of alumina ceramic crucibles, CSCERAMIC recognizes the nuanced considerations that come into play when choosing the ideal crucible for melting precious metals. This section will delve even deeper into the crucial factors that demand meticulous attention.
Temperature Uniformity and Precision
When working with precious metals, achieving precise temperature control is essential. Alumina ceramic crucibles excel in maintaining uniform temperature distribution within the crucible, leading to consistent melting results. This is particularly vital for alloys with intricate phase diagrams and narrow melting temperature ranges. The ability of alumina ceramic crucibles to provide a stable and evenly heated environment ensures that the precious metals undergo the desired transformation with minimal risk of temperature-related issues.
Avoiding Contamination
The purity of precious metals is of paramount importance in various industries, such as electronics and jewelry. Alumina ceramic crucibles shine in this aspect, as their inherent chemical inertness prevents any leaching or contamination of the molten metals. This ensures that the end product retains the intended composition, meeting the highest quality standards.
Comparative Analysis with Other Crucible Materials
A comprehensive analysis of alumina ceramic crucibles alongside other crucible materials reveals the superiority of alumina ceramics in specific scenarios, especially when dealing with precious metals and high-temperature applications.
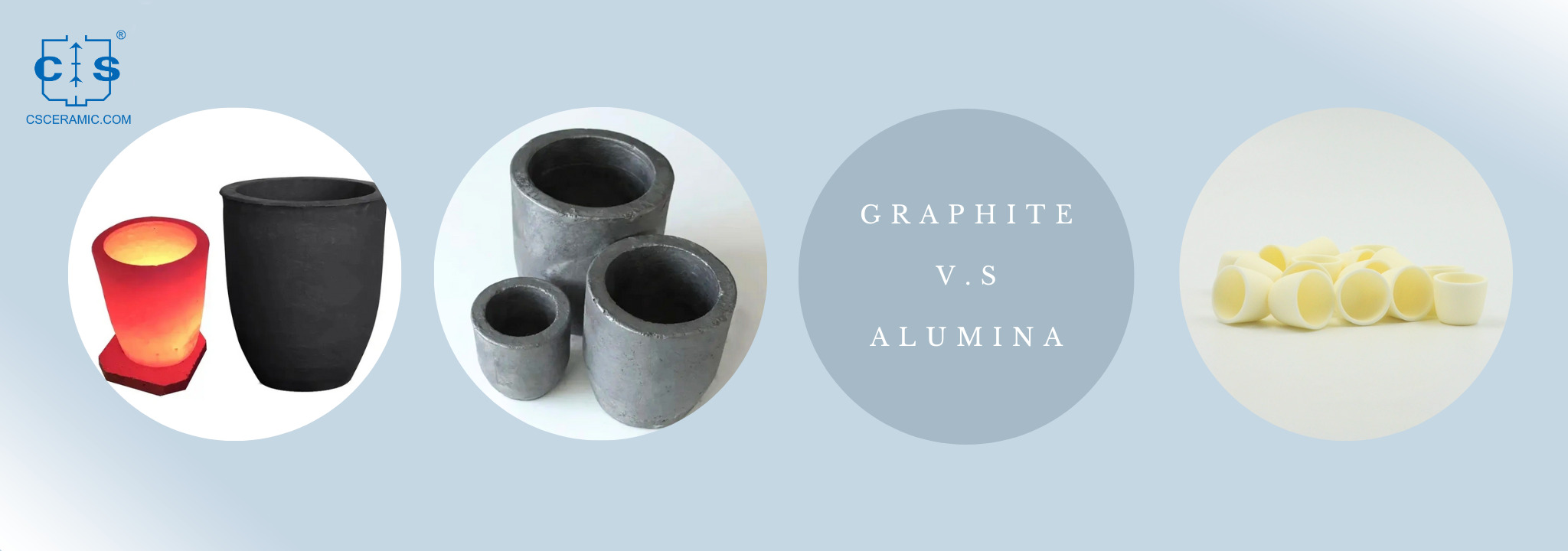
Graphite Crucibles
When it comes to choosing the right crucible material for melting precious metals, the comparison between graphite and alumina crucibles is a critical consideration. Both materials have unique characteristics, and understanding their differences is essential for making an informed decision.
-
Thermal Conductivity
Graphite crucibles are renowned for their excellent thermal conductivity. This property allows them to efficiently transfer heat to the molten metal, facilitating faster melting processes. However, in applications where precise temperature control is paramount, such as alloys with specific melting points, the high thermal conductivity of graphite crucibles may pose challenges. Alumina crucibles, while not as thermally conductive as graphite, offer better temperature stability, making them a preferred choice when maintaining consistent temperatures is crucial.
-
Chemical Inertness
Alumina crucibles have a distinct advantage in terms of chemical inertness. They are highly resistant to chemical reactions with molten metals, ensuring the purity of the melted material. This property is particularly significant for industries such as jewelry making and semiconductor manufacturing, where even minute impurities can impact the final product's quality. Graphite crucibles, on the other hand, can introduce carbon contamination into the molten metal, making them less suitable for applications where purity is a top priority.
-
Mechanical Strength
Graphite crucibles exhibit good mechanical strength, making them capable of withstanding mechanical stresses during handling and thermal cycling. However, in high-temperature applications, graphite crucibles tend to undergo wear and tear over time, which can affect their longevity. Alumina crucibles, known for their robustness and ability to withstand extreme temperatures without significant deformation, offer a longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of crucible replacements.
-
Cost Considerations
Graphite crucibles are generally more cost-effective than alumina crucibles. This cost difference may be a crucial factor for industries with budget constraints. However, it's essential to weigh the cost savings against the potential trade-offs in terms of purity, temperature control, and longevity, depending on the specific needs of the application.
-
Application-Specific Considerations
Choosing between graphite and alumina crucibles depends on the specific requirements of the melting process and the industry in question. Graphite crucibles may be preferred for rapid melting in applications where the introduction of small impurities is acceptable, and cost efficiency is essential. Alumina crucibles, with their superior purity preservation and temperature stability, are ideal for applications that demand high levels of precision, consistency, and purity.
Zirconia Crucibles
While both zirconia and alumina crucibles offer remarkable properties, a direct comparison reveals some key distinctions:

-
Thermal Conductivity
Zirconia has slightly lower thermal conductivity compared to alumina. While this can be advantageous in some situations, it may require adjustments in heating protocols for optimal performance.
-
Mechanical Strength
Alumina crucibles typically have higher mechanical strength compared to zirconia crucibles. This can be important in applications where the crucible may experience mechanical stress.
-
Cost
Zirconia crucibles are generally more expensive to produce than alumina crucibles. This cost difference may influence the choice of crucible material based on the specific budget constraints of the application.
-
Specific Applications
Zirconia crucibles are particularly well-suited for extremely high-temperature applications, while alumina crucibles may be favored when a balance between temperature resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness is desired.
Applications Beyond Precious Metal Melting
The versatility of alumina ceramic crucibles extends far beyond the realm of precious metals. They play a vital role in diverse industries, driven by their exceptional properties and reliability.
Advanced Ceramics Production
In the production of advanced ceramics, alumina ceramic crucibles offer an ideal environment for sintering and shaping high-performance ceramic materials. The ability to endure high temperatures without compromising the ceramics' structural integrity is invaluable.
Glass Melting
The glass industry benefits from alumina ceramic crucibles in the melting and refining of specialty glasses. These crucibles maintain the purity of the glass, ensuring that the final product meets stringent quality requirements.
Laboratory Research
In research settings, alumina ceramic crucibles serve as indispensable tools for conducting experiments involving extreme temperatures and the need for a non-contaminating environment. Researchers across various disciplines rely on the consistency and reliability of alumina ceramic crucibles.
Conclusion
Alumina ceramic crucibles present a compelling option for melting precious metals, offering exceptional temperature resistance, chemical inertness, and purity preservation. Their versatility extends beyond precious metals, making them an asset in diverse industries.
Thank you for reading. We invite you to visit CSCERAMIC for more information if you would like to learn more about industrial ceramic material and the advanced range of ceramic products we offer.


 info@csceramic.com
info@csceramic.com







 +86 18273288522
+86 18273288522